Amongst the innovations and technologies this century has provided to the world, the Internet surely tops the list. What started as a primary and accessible mode of communication for the military has now evolved into a giant multitude of connections, computers, and servers.
Internet, in general, is composed of thousands of different components, and DNS is among one of its most important ones.
What is DNS?
DNS abbreviates for Domain Name System. It can be simply defined as “the phonebook of the Internet”.Like a phonebook that saves both the names and phone numbers of the person, the DNS keeps domain names and their corresponding IP addresses. With a DNS directory, an Internet user does not have to remember complex IP addresses, as he can remember the name of the domain that is much simpler and easier.
Example of DNS to IP Conversion:
Whenever we enter our desired web page’s name in the search bar (e.g., www.example.com), the DNS directory converts it into an IP address (193.128.1.2). This conversion helps the user to locate the domain on the Internet.
How is DNS Cache Generated?
DNS cache is a local directory or a database generated by your computer’s Operating System (OS). This database records all the recent visits you have made recently to the different websites and Internet domains. Like a phonebook that allows you to view the names and addresses of your contacts without memorizing them, the DNS directory saves you from remembering the complex IP addresses of every website.
How to Clear DNS Cache?
In this section of the article, we have discussed cache cleaning methods for macOS, Windows, Linux, and Google Chrome, respectively.

Clear DNS Cache On Mac
Before clearing DAS Cache on mac, you might wonder to know why we should clear DNS Cache on Mac?
Under normal circumstances, there isn’t any need for you to clear your computer’s DNS directory. But sometimes, a website can change its DNS server address. And since our computers are unaware of this change, they keep the record of the old DNS directory. This, in turn, creates problems in accessing the website. Therefore, we need to clear and update the DNS cache of our computers manually.
After you flush the DNS cache on Mac, your computer will not have any trouble revisiting the website with DNS change.
You can quickly clear your DNS cache on Mac by using Umate Mac Cleaner. It not only helps you to clear your DNS cache but also erases your private data. To use Umate Mac Cleaner, follow these steps:
Step 1.Install and launch Umate Mac Cleaner on your Mac.
Step 2.Select the tab “Erase Private Data” and click "Scan"; Umate will locate the traces of DNS files and other private files.
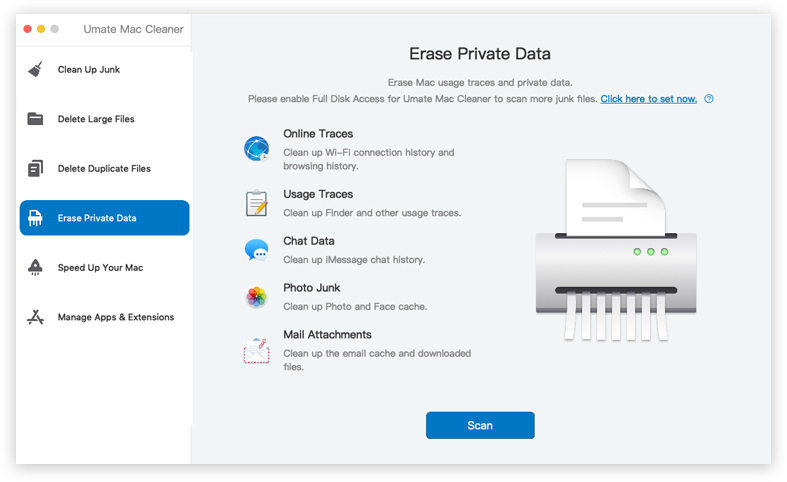
Once the list is open in front of you, choose the files you want to get rid of and click “Erase.”
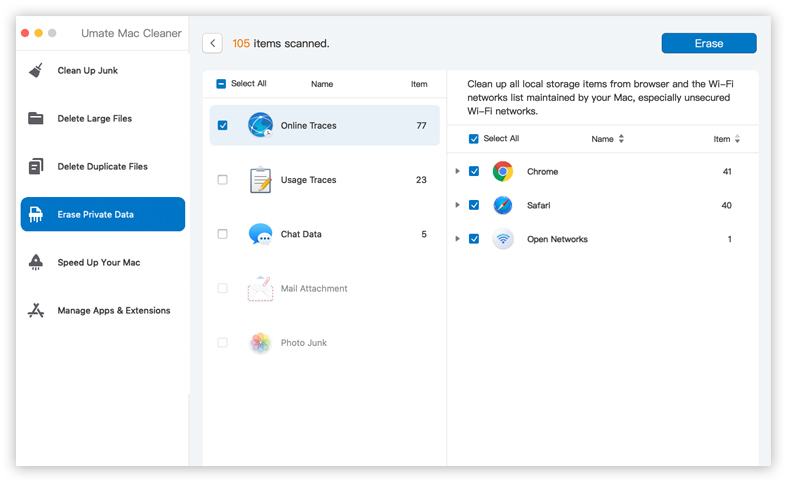
Which Mac Devices can run the Umate Mac Cleaner?
1. Umate Mac Cleaner is supported by the following devices:
- Open The Finder's Program
- Mac Book
- MacBook Air
- MacBook Pro
- iMAC
- iMac Pro
- Mac Pro
- Mac Mini
2. The following OS support Umate Mac Cleaner:
- Big Sur (macOS 11)
- Catalina (macOS 10.15)
- Mojave (macOS 10.14)
- High Sierra (macOS 10.13)
- Sierra (macOS 10.12)
- El Capitan (macOS X 10.11)
- Mavericks (macOS X 10.9).
Note: Umate Mac Cleaner can help cleaning System Cache files as well as Browser Cache files.
Clear DNS Cache On Windows
Flushing the DNS cache in Windows is a very simple and easy process. What’s more impressive is that this method applies to all versions of Windows.
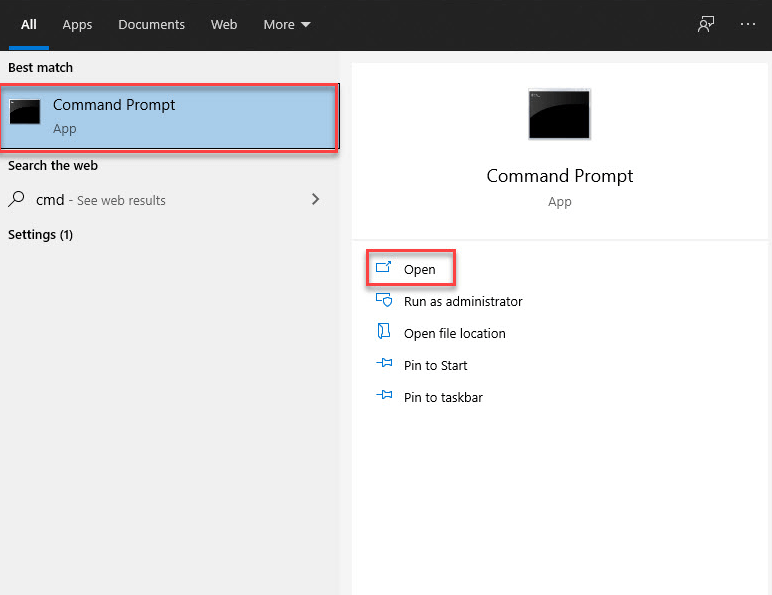
To initiate the flush DNS command on your Windows, follow these steps:
Step 1.Load the “Command Prompt” as the administrator of your computer. You can do this by typing “Command Prompt” in the “Start Menu.”
Step 2.Once the prompt loads, type “ipconfig/flushdns” and then press “Enter.”
Step 3.The “DNS Resolver Cache” confirmation message will appear once the process is completed.
Clear DNS Cache On Linux
Linux computers have a different configuration than Mac and Windows computers. In Linux machines, some distributions use a different DNS service, while others may not use a distribution service at all.
How to Clear DNS Cache for Different Linux Distributions:
Linux machines have different services on their distribution, such as
- NCSD (Name Service Caching Daemon)
- BIND (Berkley Internet Name Domain)
- dnsmasq
Clearing DNS cache for every DNS requires launching a terminal window. Pressing “Ctrl+Alt+T” on the keyboard to use the relative command for flushing the DNS cache on your Linux computer
Linux Flush DNS: For NCSD:
For flushing the NCSD DNS cache, enter the following command:
sudo /etc/init.d/ncsd restart If the terminal asks, enter your password. The process will stop and then starts the NCSDservice within a very short time.
Linux Flush DNS: For BIND:
To flush DNS for your BIND cache, you can use different flush DNS commands such as
- sudo /etc/init.d/named restart
- sudo rndc restart
- sudo rndc exec
To finish the process, you may need to enter your password. One thing you can find while clearing DNS cache on BIND is that it allows you to target specific domains. To do so, add “flushname” and the domain name in the “sudo rndc” command.
E.g., sudo rndc flushname example.comLinux Flush DNS: For dnsmasq:
To clear the dnsmasq cache, use the following flush DNS command:
sudo /etc/init.d/dnsmasq restart.
The terminal may ask you to enter your password again.
Clear DNS Cache On Google Chrome

The DNS cache stored by Google Chrome is different from the OS of the computer.
Step 1.
Type the following chrome://net-internals/#dns in your browser’s address and hit Enter.
Step 2.
Find and click the button “Clear Host Cache” to clear your Chrome’s DNS cache.
Conclusion
Internet is not a simple communication tool it used to be. Because of this complexity, computers and other devices now face regular problems with Internet use. Although troublesome, these problems can be easily resolved by performing simple tasks, such as flushing DNS cache.
We sincerely hope that the steps and methods presented above for flushing your DNS cache will be helpful for you. As mentioned above, the DNS is one of the core components of the modern Internet. Flushing it regularly can help your browser function in a better way.



















 August 12, 2021
August 12, 2021

